Skip to main content
Friday Optional Lecture 3 (9/26/2025)
Lecture 11
- Elongation factors
- EF1
- Can be used to increase the speed of translation
- EF2
- EF-Tu
- EF-G
- Met-tRNAi
- Translation initiation
- Eukaryotes use methionine
- Prokaryotes use formylmethionine
- Translation happens when the ribosome slides from the 5' end to the initiator sequence, where it begins to translate the RNA to proteins
- eIF2 is removed when the ribosome binds to the initiator sequence
- Methionine has to be in the P site
- Leaky scanning
- Shine-Dalgarno
- Peptidyl transferase
- The RF1 is used at the A site, then the P site, which destabilizes and deconstructs the ribosome
- hsp60 is the "chaperonin"
- Barrel chamber
- Isolation chamber
- Proteasome
- Inside the cytoplasm generally
- Inside the proteasome, unfoldase unfolds the protein into a linear form
- Depending on where you put the ubiquitin, you get different results
- 26S proteasome
- Made of two 19S (one on each side as a cap) and one 20S proteasome
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Likely only MCQ, but possibly integrated in a free response question, but only as a setup for the question
- Cystic fibrosis
- Likely only MCQ, but possibly integrated in a free response question, but only as a setup for the question
Lecture 12
- Transcription regulators
- Know the types of transcription regulators
- The “breathing” of nucleosomes helps to express different genes
- Tryptophan
- Will not be asked the structure
- Just know that it is the largest out of the 20 common ones
- It has only one codon
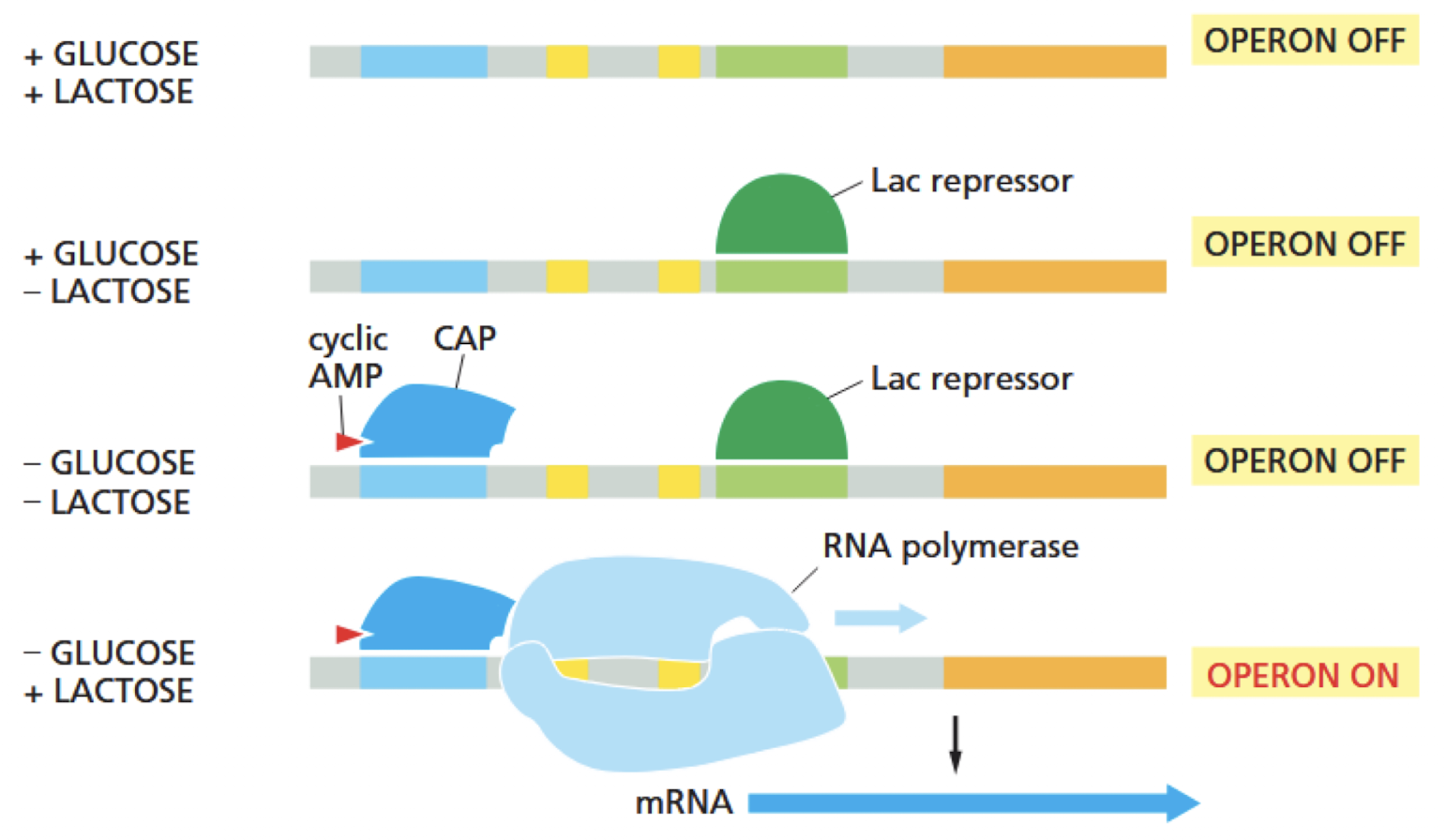
- Lac Operon
- Know what happens with the different glucose and lactose levels
- Tryptophan is used for regulation occasionally
- DNA bent around a mediator complex can give it a lot of variability
- Transcription can recruit a nucleosome-related protein to help modify the gene
- Lysine is used a lot in the relationship between nucleosomes and transcription
- Transcription repressors
- Riboswitches
- RNA folding leads to regulatory activity
- Folds to bind to small molecules for activation
- RNA editing
- The deamination of adenine to inosine (hypoxanthine + ribose)
- Apolipoprotein B
- Can change C to a U or vice versa. These are used for RNA editing and can change the location of the where the resulting protein should be used.