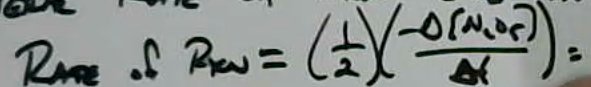Skip to main content
Chapter 14
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics
Rates of reaction and the particulate nature of matter
- Kinetics:
- Rates of reaction (speed)
- The sequential steps of a reaction
- Affect the rates?
- Concentration of the reactants
- The more stuff that is present, the more collisions will occur and the rate of reaction will increase
- Temperature of reaction
- As the temperature increases, the rates also increase
- Structure and orientation of particles
- B-A + C
--->→ A-C + B
- A-B + C -/->
Rates in a chemical reaction
- Rate = $\frac{\text{Concentration Change}}{\text{Time Change}}$
- 2 N2O5
->→ 4NO2 + O2
- Rate of formation for NO2: $\frac{\Delta [NO_2]}{\Delta t} = 3.7\times 10^{-5} M s^{-1}$
- Rate for formation for O2: $9.00\times 10 ^{-6} M s^{-1}$
- Rates must be positive
- General rate of reaction
- Instantaneous rate: rate of reaction at a single point in time
- It is the slope tangent to the curve
-